
“There’s no need to act hastily.” –CDCR counsel Kathleen Walton
“Yes there is. Yes there is. There is a need to act hastily.” –Justice Kline, CA 1st District Court of Appeal
Oral Argument, In re Von Staich on Habeas Corpus, September 8, 2020
Today, the First District Court of Appeal heard oral argument in In re Von Staich, the San Quentin COVID-related habeas case. The hearing opened with a legal debate on whether CDCR, who disputes the declarations and reports made by physicians about the conditions at San Quentin, should have provided actual evidence to refute these reports. CDCR representative Kathleen Walton argued that the habeas rules did not require her to provide these facts, and pressed the court for an evidentiary hearing; Brad O’Connell, for the petitioner, argued that CDCR made no attempt to plead the facts or meet them at all. Justice Kline characterized the prison’s response as “conclusionary statements, not facts”, and rejected CDCR’s argument that the issues they briefed on (whether CDCR provided adequate cleaning, sanitizing, masks, continuation of of holding petitioner Von Staich with other inmates, whether COVID is still spreading at the prison, etc.), were the focus of the case. “What we believe this case is about”, said Justice Kline, “is whether there is persuasive evidence that the court must do what the Plata court cannot do, which is to reduce population of San Quentin to a level that can permit the administration of social distancing within that prison.”
After confirming that CDCR can, indeed, release people serving life with parole, and discussing the legal mechanisms to do so (including the Governor’s emergency authority to release), much of the discussion consisted of CDCR peddling various falsehoods and the Justices not having it. At some point, Ms. Walton intimated that they estimate that some of their vigorous efforts to contain COVID in prison were hindered (they don’t know to what extent) by “inmates refusing to cooperate”, including testing and reporting symptoms. Justice Kline countered with the possibility that people were disincentivized from cooperating because the prison relied on spaces with a punitive connotation (solitary confinement cells) for the purpose of medical isolation (a problem pointed out in the AMEND report and in our Amicus brief.) This struck me as a problem that correctional health professionals should have perhaps taken into account *back in March* when they were repeatedly warned of outbreaks in prison. Fancy that, prison health officials having to consider the possibility that people might try to avoid being transferred to solitary!
Discussion then turned to release policies, with Justice Kline extensively mentioning our brief, which highlighted the most obvious demographic for successful releases: aging people doing long stints for violent crime. The AG representative responded that the petitioner in this particular case was judged to be “moderate risk.”
The next topic on the table was, again, the argument that the court was an inappropriate forum, and somehow “duplicative” of the Plata litigation. Justice Kline explained: “You keep making arguments that assume we have the same interests as the federal court. We are not being asked to evaluate the quality of care and attention to covid they are providing. [The federal courts] are looking into that.” To top the outrage, the CDCR representative tried to spin Judge Tigar’s Plata stance as “he didn’t find an Eighth Amendment violation.” Justice Kline wasn’t having any of it and responded that it is a matter of public knowledge that Judge Tigar *urged* state courts to do something because the PLRA stopped him from acting. In short, said Justice Kline, the COVID crisis at Quentin is a state prboelm, happening at a state department of corrections, which is the duty of state courts to address–in particular at Quentin, which is unique in being the system’s oldest and most dilapidated prison.
Justice Stewart then challenged the CDCR representative, quoting our argument in our Amicus brief that they have basically arrived at each of the three courts handling these lawsuits and argued it was not the appropriate forum. The CDCR representative, in turn, tried to harmonize their position by creating a hierarchy of sorts between the different litigation efforts.
Even though this was, overall, a good day for the petitioner, the court did press petitioner’s representatives on the appropriate remedy. Issuing an order to release 50% of the prisoners, said Justice Kline, is “something I’m not sure I’m willing to do. . . not confident that my court has the ability.” Indeed, the role of the appellate court might be limited to assessing whether the current conditions at Quentin allow the social distancing necessary to stop the spread in that facility, and to put in some guidelines about particular issues that would apply across the board. Justice Kline also commented that the lawsuit has already resulted in a benefit to Von Staich himself; he’s been isolated and no longer as exposed to COVID as he previously was. In light of these issues, the question to petitioner’s attorneys was, “What would you have us say?” The response from Richard Braucher (for the petitioner) was that the only ways to reduce the population at Quentin were via release or via transfer.
Which is where the argument for petitioner touched on some real talk. The elephant in the room, of course, is the rise in cases at other institutions not at stake in this lawsuit. Petitioner’s representative specifically mentioned the situation at Avenal, which has become dire in the last few days, and is currently the worst COVID Petri dish in the state. Here’s the picture there:
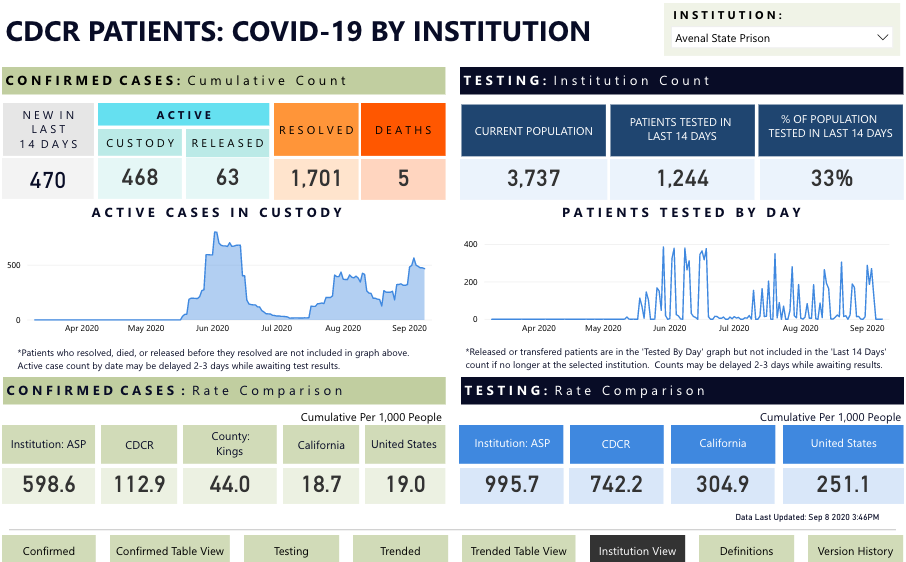
We’ve been tracking the CDCR prisons as well as CA counties for months now, and I should probably say that I’m not at all sure whether this is a third outbreak or the continuation of the second one; testing has been sporadic and erratic and basically reflects Trump’s philosophy of “no testing –> no cases.” Nonetheless, it indicates active disease, and it’s not the only place with hundreds of cases. Folsom is doing abysmally as well:
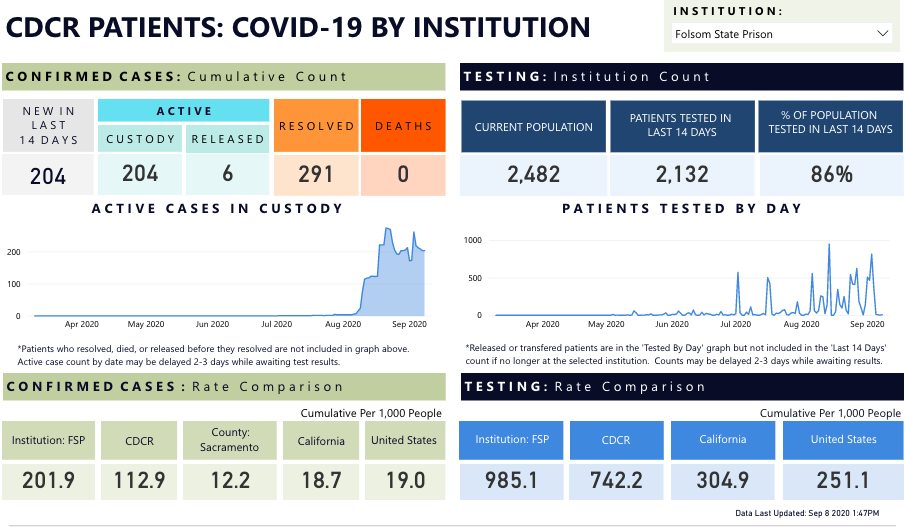
The Court, however, expressed the need to restrain the extent of their inteference with prison business via a direct release order. They pressed petitioner’s representatives on this point, and I think I would have argued that CDCR *needs* help and guidance from the courts because it had *ample* opportunity to do the decent thing and didn’t do so. Even the current CDCR plan is dated, inadequate, targets the wrong people, and we now hear will take the better part of a year to implement, which will come woefully late for the folks who will get sick or even die in the interim. That launched a discussion of how petitioner’s counsel would craft the priority of releases, to which they replied that the two lynchpins of the policy should be age and medical condition.
This opened the door to some breathtakingly cynical takes from the CDCR representative, the gist of which was that there was “no need to act hastily”–presumably because the urgent call to release 50% of the people in prison happened before the reductions in population and because now, after so much damage has already been done, they’re implementing some new program for sanitation and PPE equipment. Basing an argument that no remedy should be offered on the fact that the harm’s already been done was pretty much what I expected them to argue; CDCR has maintained that they are winning the fight against the virus, when in fact the virus has already won and continues to win, again and again, in prisons where COVID was thought to have abated. Justice Kline responded from the heart: “Yes there is. Yes there is. There is a need to act hastily.” People have gotten sick and died, he said, and we must ensure that no more of this happens. We now wait to hear what the Court will decide.



No comment yet, add your voice below!