
A Sanhedrin that executes a transgressor once in seven years is characterized as a destructive tribunal.
Mishna Makkot 1-10
So too for those who are liable for capital punishment or lashes: their death or lashing does not atone for them until they repent [do teshuvah] and confess verbally [do vidui].
Mishne Torah LaRambam, Repentance 1:1
It’s hardly debatable that Richard Nixon’s presidency was a watershed moment in American criminal justice. Even the scholars who point to punitive tendencies among his predecessors will admit that Nixon’s presidential campaign highlighted crime—and particularly judicial permissiveness in the face of rising crime rates—as a key political issue, and that his presidency made good on the promises to become tougher on crime.
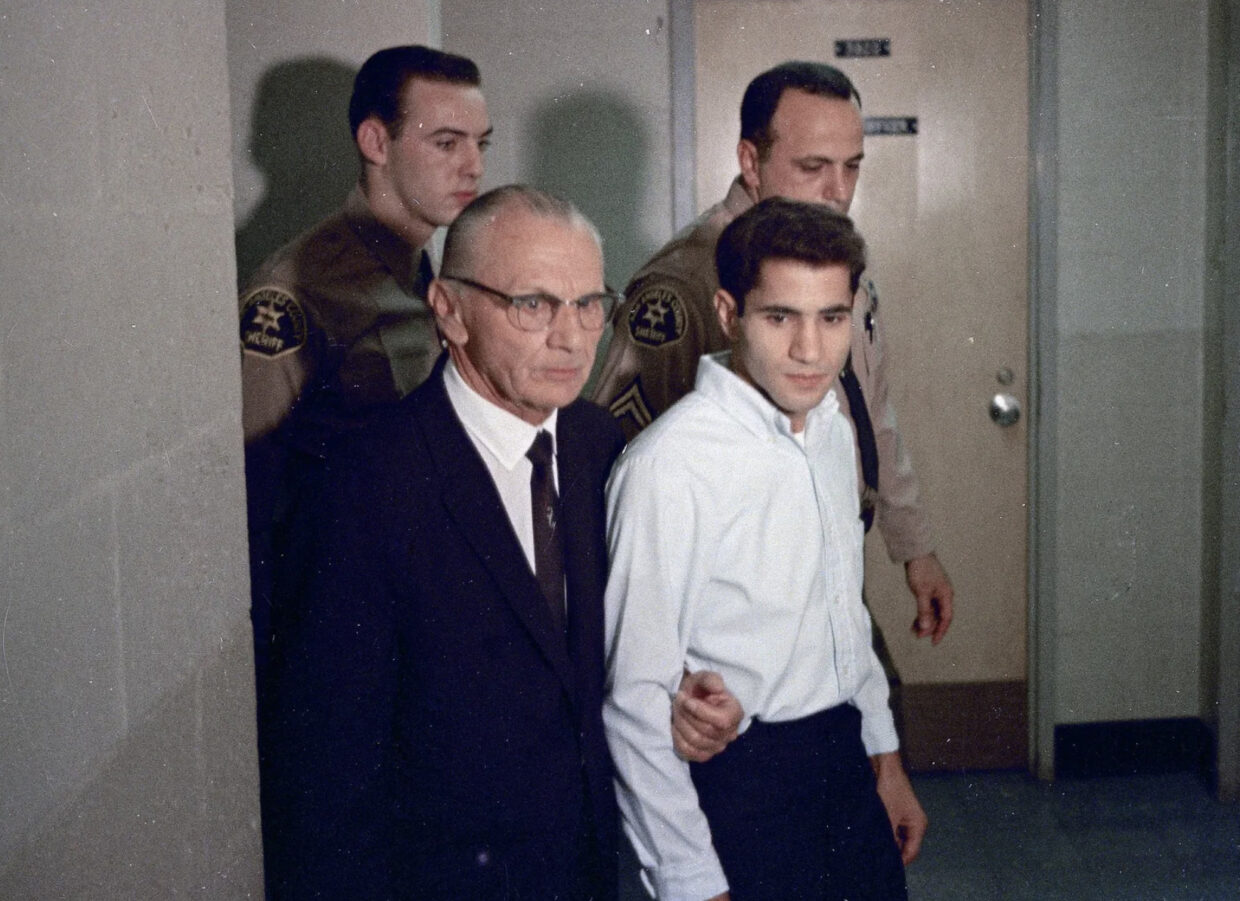
Having lived under this regime for 50 years, it’s hard to speculate what our system would look like if Nixon had not been elected. We did come very close: Nixon’s most promising challenger for the presidency was Democratic Senator Robert Kennedy, well-respected and admired, and a former Attorney General. But shortly after Kennedy announced his victory in the California Democratic Primary at an event at the Embassy Hotel, a young Palestinian refugee, Sirhan Sirhan, darted toward the Senator and fired several shots from his revolver. Kennedy was killed and four other people were injured by the gunfire.
Sirhan was sentenced to death, but experienced a stunning reversal of fortune. In 1972, the California Supreme Court found the death penalty unconstitutional, and the 107 people on death row at the time–including the Manson family members and Pinole murderer Dennis Stanworth–had their sentences commuted to life with parole. By the time California brought the death penalty back in 1978, alongside the option of life without parole, the “Class of ’72” people were already preparing for their upcoming parole hearings. One of them was Sirhan Sirhan.
Almost immediately after his arrest, and throughout his trial and incarceration, Sirhan was interviewed by many psychiatrists. They noted his traumatic childhood in Palestine, his harrowing journey to Jordan as a refugee, the horrendous violence he witnessed as a young child. They identified psychosis and paranoia. But by the mid-1970s, he seemed to settle down, to the point that the parole board–on par with how things were done in those days–sat down to set a parole date for him. They settled on 1984; 16 years was plenty for first-degree murder back in those days. If this seems oddly lenient to you, keep in mind that Sharon Tate’s family members thought it would be an uphill battle to keep the Manson girls behind bars in 1978.
Sirhan’s early hearings in the late 1970s were basically status conferences, which followed up on his rehabilitative journey in prison. But things took an interesting turn in 1982. On April 26, a Monday, the parole board convened for a week-long hearing in his case, whose purpose would be to determine whether to rescind his 1984 parole date.
The impetus for this unusual step was threefold. First, as Sirhan’s release date approached, the Board faced unexpected gale force winds of public disapproval. The Commissioners received of 3,961 letters; 8,127 signatures of petitions; and 50 city and county resolutions requesting the recission of Sirhan’s parole date. The November 1981 assassination of Egyptian president Anwar Sadat, on the heels of his historical peace agreement with Israel, reminded the public of yet another anti-Israel act of terrorism, spurring these letters on and drawing connections between the two acts.
Second, the Board explained, new evidence had come to light that called into question the prior portrayal of Sirhan as a docile, rehabilitated inmate. The information included a Playboy article called “inside Sirhan”, as well as numerous threatening letters Sirhan had sent from prison to various individuals, and documentation of his threatening personality in his central file. “Generally,” the Commissioners explained, “the information specified above alleges that Sirhan has made threats against various people, and that he has exhibited other behavior indicating that he is not suitable for parole.”
The third ground for the hearing, however, was legal: the board maintained that its 1975 predecessor, which set Sirhan’s 1984 date, erred in exercising its authority. The question for discussion would be: “[D]id the parole granting panels fail to exercise independent discretion in finding Sirhan suitable or in establishing a period of confinement? The panel’s failing to consider the nature of the offense and the victim in finding Sirhan suitable for or in establishing a period of confinement.” The Board answered this question in the affirmative: they claimed that the 1975 Board abused its discretion by “fail[ing] to appreciate and fully assess the magnitude of the crime for which Sirhan was convicted.”
Sirhan’s attorney, Luke McKissack, balked at these reasons for recission. All the details about Sirhan’s crime, its seriousness, and its magnitude, he said, were widely known at the time of his trial and had no place at his parole hearing. As to Sirhan’s presumably threatening behaviors, McKissack explained, they should be understood in the context of his traumatic upbringing and unusual confinement situation. McKissack recounted some of Sirhan’s traumatizing experiences in Palestine—killings, mutilations, and mass atrocities, which “Sirhan, at four years of age, obviously would be affected by seeing that kind of violence.” He also explained that Sirhan’s threats should not be taken seriously: his 14 years in protective custody “could be the equivalent of twenty or twenty-five years for somebody else. . . from the onset he knew that anybody might kill him” and his threats should be seen as what they were: the airing of frustrations made “ten years ago when Sirhan was depressed, psychologically disturbed and reflective of that situation and not as high-powered as the district attorney makes it out to be.” During those years, McKissack explained, Sirhan witnessed other people—some convicted of multiple murders—being paroled, and it was understandable that he was frustrated and felt that he was singled out: “It doesn’t seem to me that in order to qualify for being paroled, that a person has to think that everything that occurred to him in life is fair.” Sadat’s assassination, he said, had nothing to do with Sirhan, who was being scapegoated: “In 1982, in an election year, with international events out of control, everybody is frustrated. It’s: Find someone to jump on.”
The Board was undeterred. On April 27, 1982, the Commissioners interrogated their predecessor, James Hoover, a member of the committee that set Sirhan’s original parole date. The resulting exchange reads like a remarkable showdown between the rehabilitative, professional, low-key logics of 1970s parole decisions, and the much more emotional and political tenor these decisions would reflect in the 1980s. Hoover had no love for Sirhan, obviously, but he thought his job was to judge Sirhan impartially on the basis of his prison performance:
Brown: It was your impression from 75-20 that everyone had to have a parole date set?
Hoover: That was my impression, as long as there was no negative factors in file.
Brown: Initially you could find no reason to deny the setting of the parole date?
Hoover: I could find no reason. I might mention in my own mind that I wanted to find a reason. . .
You have got to remember that our median time for murder first was only about fifteen years. So that means we had an awful lot of low cases and an awful lot of high cases. . . our legislature in their great wisdom did not say, “Well, if you shot a Senator you ought to do so many years. And if you shot Jose Gonzales down in the barrio, you only do this many years”. . . At that period of time this was what was acceptable. It may not be acceptable today, but at that period of time that was the guidelines. And my feeling was, there was nothing to justify. . . I thought that was ample punishment picking that period of time, that time in space of society and what people expected.
Hoover didn’t want Sirhan to walk, but he did what he thought was his job:
W]hen I saw [the psychiatrist], I said, first thing out of my mouth, ‘Shit. This son-of-a-bitch ain’t going nowhere.’ That was just—it was the flash that came up. And then I think she said, ‘Well, show me why not.’ And that’s when I went to the file. I thought, certainly I’ll be able to have all these negative things in file. I mean, it was just set in my mind. I just walked into it and without review, just off the top of my head.
Hoover’s 1982 colleagues, needless to say, did not see eye to eye with him on this. They rescinded his date, citing not only his threatening behavior but also the 1975 Board’s mistake in discounting the magnitude of his crime. The New York Times story about the recission features clearly retributive rationales:
‘’The people of the world will breathe a sigh of relief tonight because Sirhan will remain in prison,’’ said District Attorney John Van de Kamp of Los Angeles, who had pushed for canceling the Sirhan parole date. ‘’The message must be sent out in clear and unmistakable terms that political assassination will not be tolerated in this society – and those who engage in it must pay the price.’’
‘’He deserves never to be set free,’’ said State Treasurer Jesse Unruh, who as the California manager of Robert Kennedy’s campaign for the 1968 Democratic Presidential nomination was present when the New York senator was shot. ‘’I’ve been battling that parole date since 1975.’’
As we all know, Sirhan, who is now 79 years old, remains behind bars. In 2021 he was recommended for parole, but Governor Newsom reversed; in 2023 he was again found unsuitable for parole. In his last few hearings–probably to heed the California Supreme Court’s admonishment in Lawrence–the Board stopped citing the magnitude of the crime and started giving us, instead, the usual parole word salad about insight and accountability and looking inward, the whole psychic excavation enchilada. But the archaeology of the hearings plainly shows what happened: as of 1982, the parole board started seeing itself responsible not just for assessing the parole candidate’s prison journey, but for curating and appeasing the public sentiment about his or her crime.
To be honest, I’m not sure retribution has no place in release decisions. While working on Sirhan’s parole hearings, I repeatedly thought of another political assassin: Yigal Amir, the third-year Israeli law student who assassinated Prime Minister Itzhak Rabin. In 2023, it is hard to not see Rabin’s assassination as the watershed moment that ushered Binyamin Netanyahu’s ascendance to state leadership and, as Israel faces a severe constitutional crisis that threatens to disproportionately affect Palestinians and other non-Jews, to balk at the possibility that Amir should ever be paroled. In the following video, an excerpt from an excellent satirical show called The Chamber Quintet, actor Rami Heuberger depicts Yigal Amir. He smiles at the camera and said, “in twenty years, I’ll receive clemency. You know that’s true. Deep inside, you know it.” The effect is chilling:
The prospect of parole, clemency, or a pardon for Amir is not farfetched at all under the auspices of Israel’s 37th Government. Would that really be so much more horrible than a parole for Sirhan? What about when Amir is 79 years old? I’m not sure. But I also feel that we need to talk honestly about the role, if any, that retribution should play in parole decisions, and about the extent to which we entrust Board members to properly calibrate the resulting punishment in the face of political and social considerations and public upheaval. In any case, I find it poignant that Sirhan became a victim of the era of punitiveness that he ushered with a bullet.



2 Comments
See Heather Knight’s column in April 27 SF Chronicle. Another perp, different motive but very similar prison history.
Here’s the column David is referencing: https://www.sfchronicle.com/sf/bayarea/heatherknight/article/notorious-crime-sf-parole-murder-17917323.php