I am thrilled to provide this update: We won In re Von Staich, the habeas corpus case challenging CDCR’s mishandling of the COVID-19 crisis at San Quentin. Justice Kline wrote: “We agree that respondents–the Warden and CDCR–have acted with deliberate indifference and relief is warranted.” Here is an analysis of the opinion.
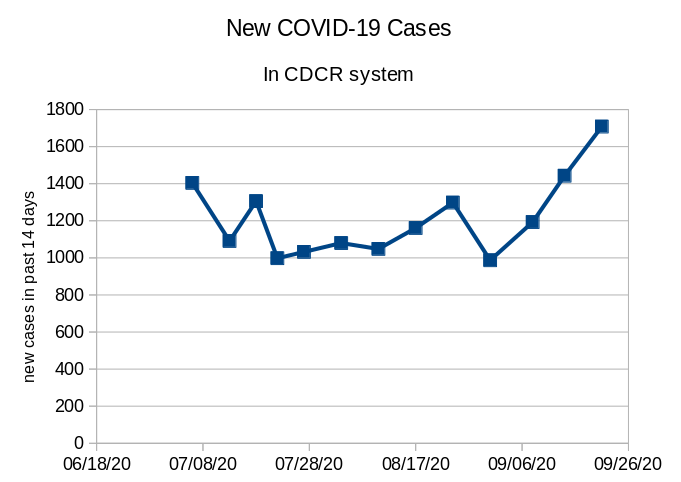
Justice Kline begins by stating the magnitude of the San Quentin catastrophe. Even against the horrific history of disease and contagion in prisons–including three separate spikes of the Spanish Flu in 1918–the San Quentin COVID-19 outbreak is “the worst epidemiological disaster in California correctional history.” He then highlights the physicians’ urgent memo (published after they visited San Quentin, at the Receiver’s invitation) recommending a 50% reduction of the prison population. CDCR’s response fell far short of this: between March and August 2020 they achieved a mere 23% reduction, “accomplished, in part, by suspending intake at San Quentin from county jails, which has increased the presence of COVID-19 in those local facilities, and is not likely sustainable.”
Justice Kline then rejects the evasive maneuvers employed by the AG’s office, who tried to play jurisdictional hide-and-seek by claiming that the San Quentin litigation effort was somehow “duplicative” of the federal case Plata v. Newsom. First, the court wrote, San Quentin is a particular, antiquated prison with specific problems, which are not the focus of the federal litigation. Second, these habeas cases are designed to ask for temporary relief, rather than the more systematic remedies sought in Plata. Third, state courts are not limited and bound by the PLRA, as federal courts are. And fourth, which I found inspiring, state courts have the duty and competence to vindicate rights under the California Constitution (which, just like the U.S. Constitution, forbids cruel and unusual punishment–albeit worded slightly differently.)
The court also rejected the AG’s office’s delay tactics, asking that the case be moved back to the Superior Court and/or that an evidentiary hearing be held. As Justice Kline explains, the AG’s declarations that the doctors have it wrong and that a 50% reduction is unnecessary were “conclusions the Attorney General has failed to support with any factual allegations contradicting petitioner’s allegations,” which were based on scientists’ and physicians’ declarations–even with testimony from their own prison physicians. Under these circumstances, “the issue before us is simply whether respondents’ disregard of the experts’ conclusion that a 50 percent population reduction is essential constitutes the ‘deliberate indifference’ necessary to sustain petitioner’s constitutional claim. The issue is one of law, not fact.”
Was CDCR’s response to the risk of infection–of which they concede they were subjectively aware–adequate? They established a central command; installed a tent structure; repurposed the chapel and a furniture factory to care for COVID-19 patients; provided PPE to the population and staff; and released 947 people. At the hearing, the AG representatives claimed that the reduction in case numbers at San Quentin was thanks to these efforts.
The Court of Appeal vehemently disagreed. Relying on the analysis of experts, the Court agreed with us that the reduction in cases was not because, but despite, CDCR’s behavior. The decision quotes Dr. Beyrer: “Had San Quentin done nothing, the rates of infection there would have been roughly the same.” And, while the steps the prison took to alleviate the risk were commendable, they were insufficient without the population reduction, which they refused to do.
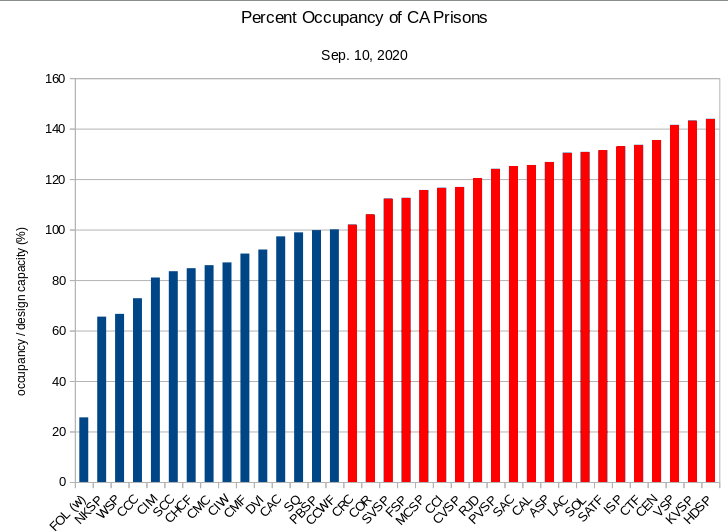
The next bit is especially interesting. The AG boasted that they managed to bring the prison population down to a bit more than 100%. Of course, as Justice Kline writes, in a facility such as San Quentin, full occupancy cannot allow for the social distancing needed to fight the pandemic. He quotes extensively from AMEND’s urgent memo, which detailed conditions in specific areas of the prison, notably North Block and West Block, showing that the combination of crowding and high-risk people was unsustainable. What interests me most about this is the extent to which the AG’s office and CDCR have become habituated to the toxic perspective according to which having their prisons 100% is a desirable end, rather than an unhealthy point of departure. We’ve had bloated prisons bursting at the seams for so long that we seem to think that a full prison at “only” 100% is fine.
The opinion then hits the nail on the head: as I explained elsewhere, the release plans are specifically designed to exclude people serving time for “a violent crime as defined by law” when such people are approximately 30% of the prison population. The AG argued that this is reasonable policy, because they, as opposed to the physicians who authored the memo, have to take into account public safety. To that, the Court has two replies. First, the prison authorities may resolve the Quentin problem not just through releases, but through transfers (though the court does mention that a botched transfer is what started this catastrophe in the first place. Second, and more importantly, even from a public safety perspective, lifers are the most obvious target population for release: they don’t pose public safety risks because they’ve aged out of crime, and they themselves face a heightened risk for COVID-19. Justice Kline writes: “Exclusion of lifers and other older prisoners who have committed violent offenses and served lengthy prison terms is also difficult to defend, given their low risk for future violence and high risk of infection and serious illness from the virus.”
Justice Kline spends several pages citing robust legal, sociological, and medical materials to show the folly of excluding lifers and strikers from release programs. He refers not only to steps taken by the CA legislature, but to the robust literature on life-course criminology, which constantly finds age a significant factor in desistance. Despite their authority to order the release of aging people who committed violent crimes, and statistics about prison demographics that they themselves provide, the AG’s insistence on mostly ignoring this category of obvious release candidates “render[s] it doubtful whether a 50 percent reduction in San Quentin’s population could soon take place.”
This behavior by prison authorities satisfies the “deliberate indifference” standard; they conceded they knew the risk, and they are recklessly failing to take the necessary steps physicians recommended, while not providing any factual justification. The continued use of spaces in which people sleep in close proximity “is not merely negligent, it is reckless”–and “the recklessness is aggravated by respondents’ refusal to consider the expedited release, or transfer, of prisoners who are serving time for violent offenses but who have aged out of a propensity for violence.”
As to petitioner, Ivan Von Staich, the Court has ordered his immediate release from San Quentin. Von Staich was recommended for parole on October 16, but the Governor can weigh his case for four months, and in the meantime he must be released or transferred to a different facility. In addition, the Court agreed that the habeas corpus process allows them to extend relief to similarly situated people. However, the Court opines that “it would be inappropriate to order the release of prisoners we considerd vulnerable even if we thought we had the power to do so in this proceeding.” The Court raises three concerns in this respect: one, that medical vulnerability is a question of “scientific facts, not law”; two, that they are unsure whether they can extend relief to people who did not file a habeas petition; and three, that the appropriate social distancing via releases/transfers can be created not only by transferring vulnerable prisoners out of San Quentin, but also by releasing other people in sufficient numbers to allow for social distancing or the remaining prisoners.
“Nevertheless,” writes Justice Kline, “we are not without means to expedite the release or transfer from San Quentin of more inmates than are now deemed eligible for release.” These means are provided by Section 1484 of the California Penal Code, which allows the Court such course of action. The Court cites numerous California cases that involved injunctive relief through Habeas. By this authority, the Court orders CDCR to bring the CDCR population down to 50%–“no more than 1,775 inmates.” The Court leaves the manner of doing so in the hands of CDCR, though Justice Kline does offer, as possibilities, “expanding eligibility for the two expedited release programs currently limited to inmates not serving sentences for violent offenses to inmates like Petitioner, who are over age 60 and completed minimum terms of at least 25 years.” Note that, despite the Court’s conciliatory words that CDCR is free to achieve the population reduction in whichever way they like, the decision discusses at length the fact that ignoring aging people serving long sentences for violent crimes is what stands in the way of achieving the desired reduction. The order specifically mentions the criteria above (over the age of 60 with 25 years incarceration) and also makes reference to the need to speed up the Elderly Parole Program.
Because of the need to act rapidly to save lives, the decision becomes final in 15 days, and the Court refers the parties to the Marin Superior Court for future disputes.