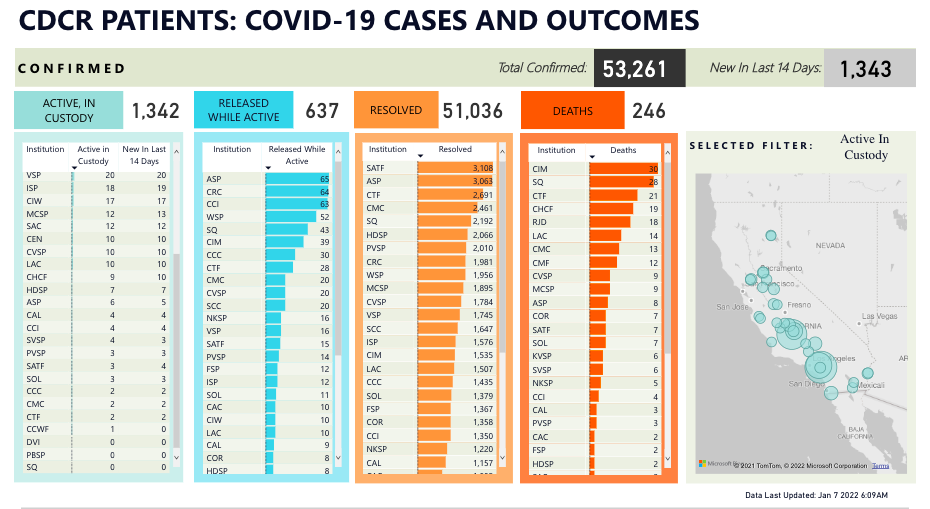
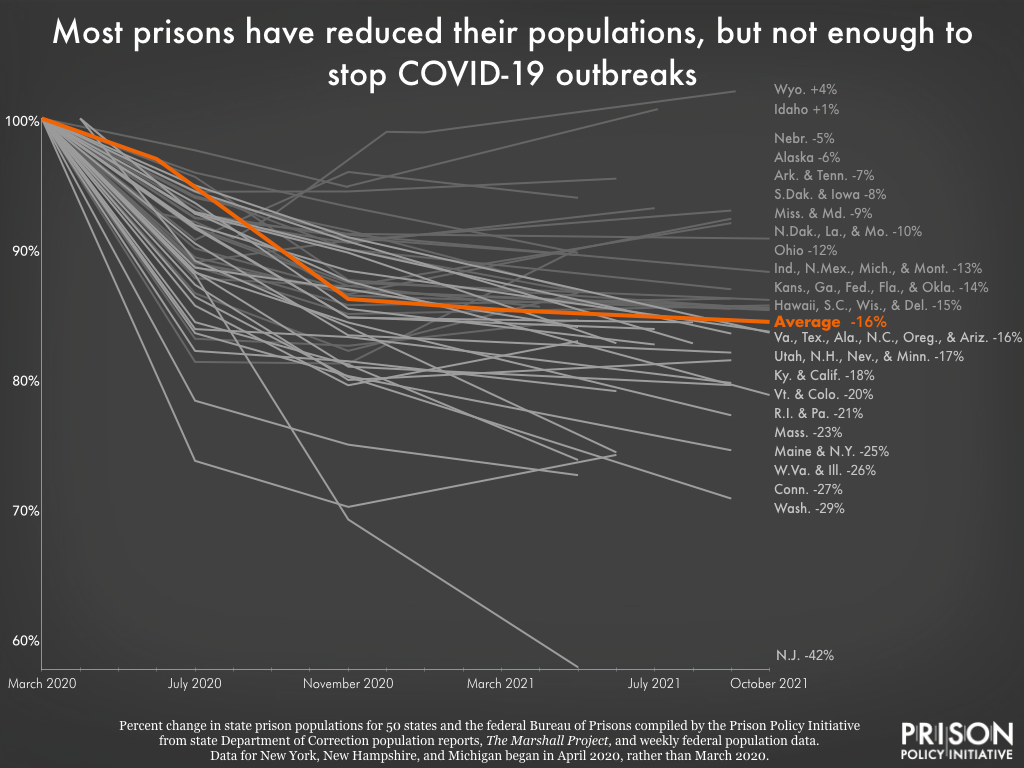
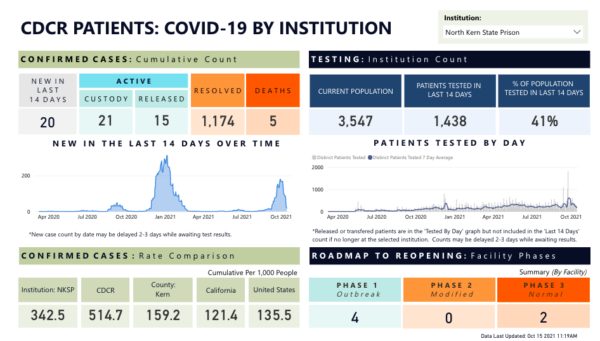
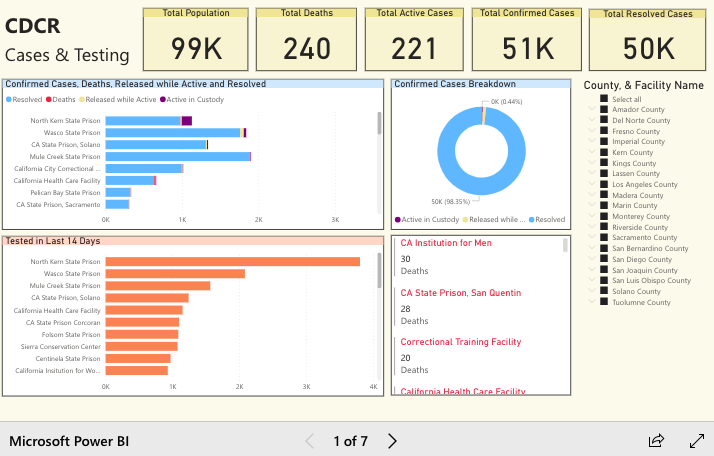
Twenty-twenty was a watershed year for conversations around criminal justice reform, abolition, and transformative justice. Calls for change gained public support in ways rarely seen before. The combined ills of COVID-19 and police brutality highlighted issues within the “criminal legal system”Footnote1 of the United States (US) that could no longer be ignored. And yet, one area of the system remains in the background: community corrections. For all the calls to reform or abolish the carceral state, the “Cinderella complex” surrounding community supervision (Robinson 2016) helps maintain these systems as public secrets (Shah 2020). One book published in 2020 that aims to shed light on issues within a part of these systems—parole—is Hadar Aviram’s Yesterday’s Monsters: The Manson Family Cases and the Illusion of Parole.
Aviram’s book makes it clear that parole, particularly parole hearings, must be a part of conversations around criminal justice reform and transformative justice, and she uses an unusual case to do so. As Aviram notes in the Preface and Acknowledgments, she never intended to write a book about the Manson Family. Similarly, many of us never intend to read a book about the Mansons. In this case, however, not doing so would be a mistake. Yes, it is a book about the Manson Family. But it is also not a book about the Manson Family. Aviram deftly uses the story and lore of the Mansons as a vehicle to take a deep dive into the very opaque process of parole hearings and release decisions. Yesterday’s Monsters: The Manson Family Cases and the Illusion of Parole is also an examination of societal views on violent offenses and an exploration of how assumptions and prejudices about those who commit such crimes haunt the US criminal legal system decades after the fact. “The too long, didn’t read” summary for Aviram’s book is: come for the Manson Family cases; stay for the carceral critique.
Aviram’s book is divided into an Introduction and seven chapters. In the Introduction, Aviram provides the impetus for the book: she notes that violent crimes are a key point of analysis because they often lead to dramatic changes in criminal justice policy; she explains why the Manson Family hearings offer a unique window into how parole hearings operate, particularly given the extensive records available; and she describes the notion of parole as a performative space as a way of framing parole hearings. The following two chapters contextualize the analysis presented in the book. Chapter One provides a fantastic crash course on parole, including its purpose, how the role of parole within corrections has changed over the years, and how the parole system operates, including the administrative side of parole and the parole hearing process, as well as how legal cases impact the process. Chapter Two takes a broader look at the California penal system and examines how the return of the death penalty in the late 1970s, the rise of victims’ rights advocacy, and cases such as those involving the Manson Family sowed the seeds for a trifecta of extreme punishments: 1) the death penalty; 2) life without parole; and 3) life through the constant denial of parole or, what Aviram (2020: 40) calls, “life de facto.” These three punishments, Aviram argues, provide the background for two key themes about parole hearings that are presented in the remaining chapters.
The first key theme, the role of narrative in parole hearings, is brought to light in Chapters Three through Six. Narrative plays a role in these hearings in four ways. First, in Chapter Three, Aviram uses narrative analysis to discuss the various stories that were used to explain the Manson Family murders and how the “Helter Skelter” narrative rose to prominence. Aviram expands this analysis in Chapter Four to show how the “Helter Skelter” narrative impacts the Manson Family’s parole hearings and the story that parole board members expect in such hearings. In Chapter Five, Aviram shows how the desire for a specific story by board members impacts parole hearings for all individuals under consideration, not just the Mansons. Finally, in Chapter Six, Aviram introduces the notion of the “Bardo”— the idea that one’s future is predicated on one’s past—and how it can be used to conceptualize the entire process of release to parole.
The analysis presented in these four chapters echoes an oft-repeated line from Hamilton: An American Musical: “Who lives? Who dies? Who tells your story?” In the case of parole hearings, who tells the story and the narrative chosen is the crux for determining who lives and who dies. As Aviram argues, the key to the narrative for all parole hearings is the notion of insight, which seems to be a stand-in for rehabilitation. Like rehabilitation (see Shah 2017), insight seems be a bullshit term as determining whether one has gained insight or is on the road to rehabilitation appears to be the criminal legal system’s equivalent of “I’ll know when I see it.” But this, ironically, requires insight on behalf of the parole board to know what they want to see and the ability to convey that to the individual being considered. Hence, both insight and rehabilitation raise questions about how success is defined and who gets to define it (see, e.g., Heidemann et al. 2015). These questions become key as the notion of “success” seems to be the basis of the narrative the board is seeking, even if that is not what they call it.
Unfortunately, for the individuals involved in the Manson Family cases, the narrative desired is also impacted by the narrative told about the crimes themselves. As Aviram notes, while the narrative that “stuck” was the “Helter Skelter” narrative, two more sympathetic and arguably more accurate narratives—that of a cult and that of common criminals—also exist. Nevertheless, the “Helter Skelter” narrative is the one used against the Manson Family members. In doing so, the parole board members and the victims and their representatives use the narrative to write a book with a predetermined ending, and no matter what the characters do or what the system allows them to do, the book will end the same way. This is made abundantly clear in the story of one Manson Family member, Susan Atkins, who, while literally on her death gurney, was still denied release for fear of her “dangerousness.”Footnote2
Indeed, adherence to the desired narrative—one that focuses on the ability to build a life in prison as expected by the parole board but one which is often difficult to achieve—reveals a frustrating Catch-22. On the one hand, the parole board requires attending programs, many of which do not exist or are not accessible because of housing and work schedules, and it dismisses the sort of self-led programming individuals participate in to try to meet this requirement. Thus, the parole board’s refusal to acknowledge the reality of life in prison is used to undermine attempts at progress and thus deny release. On the other hand, the parole board chides individuals for not obtaining specific job skills. This can lead to an undermining of parole plans—such as the case of Manson Family member Bobby Beausoleil, who showed evidence that obtaining a well-paying job is possible—which also leads to a denial of release. In other words, the narrative is set, and parole board members utilize their knowledge in ways that ensure the ending they desire.
For individuals seeking parole, the parole board’s preferred narratives also raise real questions about when or even if it possible to become an “ex” or “former,” whether it be offender or incarcerated individual. Individuals before the parole board are made to re-tell their histories over and over again, and the parole board relies heavily on the initial conviction and past infractions, risk assessments, and therapist notes when making their decision. This makes it virtually impossible for those eligible for consideration to ever become more than who they were. The “moral memory” holders present at the hearings—the prosecutors, victims, and victims’ representatives—certainly do not help in creating new narratives about the present or future.
The second key theme, the notion of the “Bardo,” appears in Chapters Six and Seven. As noted above, the concept of the “Bardo” is introduced in Chapter Six as an analogy for how one’s future is dependent on one’s past rather than one’s present. In the concluding chapter, Chapter Seven, Aviram continues this discussion, noting that the “Bardo” is a liminal space between death and rebirth. For the parole hearings, the “Bardo” is “a cycle between hope and disappointment, preparation and hibernation, action and inaction, self-improvement and self-assessment, in which inmates have to participate and lawyers act as ‘hope managers’” (Aviram 2020: 206). This cycle creates a situation where, at least during the parole hearing, individuals eligible for consideration remain stuck in a liminal space, not fully incarcerated but not yet free, both human and yet not-human. While Aviram focuses on parole, the concept of “Bardo” and analysis presented point to two larger issues within the criminal legal system as a whole: 1) the notion of the system as “effective”; and 2) the challenge of reentry to society post-release.
First, the “Bardo” raises questions about how effectiveness is measured by the parole board members and by other aspects of the system. The parole board, as Aviram highlights, focuses on a particular rationale for its decisions: an individual who is being considered for parole and has successfully completed programs and/or met the amorphous requirements the board sets for release are due solely to the successful nature of the incarceration experience. But those who fail—even when the failure is due to the systematic problems of incarceration—fail solely because of their own (in)ability to obtain proper insight and meet the unattainable requirements. In other words, the parole board deeming someone suitable for release is a testament to the idea that “prison works,” but denying release is a testament to the parole board’s role in maintaining public safety. The parole hearings are a classic case of the house always wins. But this faulty logic is precisely the logic that enables the “Bardo” to survive. The liminal space between death in prison and rebirth in society is maintained not through any real notion of making the right decisions, but through the illusion of prisons as a “correcting space” and “public safety” as a catch-all justification for carceral spaces—two terms that arguably create yet another “Bardo” and that help the board members justify their roles.
In reading Aviram’s analysis, I would argue that the notion that the house always wins can also be applied to other aspects of the criminal legal system. For probation and parole supervision, for instance, successfully navigating and being discharged from supervision is due entirely to the effectiveness of supervising agents. Getting revoked, however, is entirely the fault of the individual and a sign of the system maintaining public safety regardless of larger social factors at play. Again, the house wins. For policing, a drop in crime rates is a sign of the effectiveness of policing. A rise in the crime rate is a sign that there is not enough policing. Again, the house wins. In other words, the entire criminal legal system is a “Bardo”—one that holds society in between death (framed in language that evokes fear of crime critiques) and rebirth (framed in the language of public safety). And the language of the “Bardo” is used to maintain and justify the system’s existence and assure its continuation.
The second issue Aviram’s discussion points to is the “Bardo” of parole and reentry, more broadly. Parole, itself, is a liminal space—one that functions as a state-run reentry program: one in which an individual is free but not really free. While on parole, the conditions one must follow and the fear of revocation ensure the individual is constantly aware that he/she/they is/are still held by a sentence of the state and a reminder that the system is designed to uphold the notion that those under supervision are inherently bad and destined to fail (McNeill 2019). Furthermore, collateral consequences continue to impact them (see, e.g., Brisman 2004, 2007; Williams and Rumpf 2020). In fact, unless one’s criminal history is purged completely, all individuals with a record remain entangled in a lifelong “Bardo”: they are both in society but not of it.
Combined, the two themes regarding the role of narratives and the implications of the “Bardo” show that those sentenced to life with the possibility of parole are damned if they do and damned if they do not. Aviram highlights how life with the possibility of parole is, indeed, “life de facto”: it is essentially a life without the possibility of parole, which is, in turn, a stand-in for the death penalty. What emerges is a reminder that the system functions exactly as it was meant to. While Aviram offers suggestions for improving the parole hearing process, the analysis raises serious questions as to whether parole is a system worth saving. Thus, while Yesterday’s Monsters: The Manson Family Cases and the Illusion of Parole does not explicitly support abolitionist arguments, it could be used to do so. But that is not its only use. Aviram’s book is also a testament to the value of historical, narrative, and qualitative analysis. Scholars and students wishing to learn more about these methods, about parole, or about how to tackle the behemoth that is the criminal legal system “Bardo” will find this book a useful read.
Many thanks to Rita for this careful read and excellent review–and especially for the useful zinger “the house always wins”, which perfectly captures how parole works and what we need to fix.